Communications of the ACM
Insects Inspire Robot Design

John Schmitt and his collaborators utilize animal experiments and reduced-order locomotion models to inform robotic design.
Credit: Robert Full / University of California, Berkeley; Jonathan Clark / Florida State University
When John Schmitt looks at a fleeing cockroach, he doesn't see disease or dirt. He sees the perfect running machine. "I take my inspiration wherever I can get it," he says.
Schmitt, an assistant professor in Oregon State University's school of mechanical, industrial and manufacturing engineering, is trying to develop legged robots that can easily run over the roughest surfaces. He wants to create a robot that can run as easily as cockroaches and guinea hens, two creatures that seem to be able to do so without thinking, and without disruption.
Cockroaches, with their sprawled postures and splayed legs, slow only about 20 percent when going over blocks that are as much as three times higher than their hips. "Their remarkable locomotion performance has more to do with how they are built, rather than how they react," he says.
Schmitt and his colleagues have developed a computer model that allows a running robot to recover from a change in ground surface almost as skillfully as a guinea hen.
Furthermore, they are studying the interaction of energy storage and expenditure, sensor and feedback requirements, and leg angles to learn about recovery from perturbations--those events or obstacles that disturb motion, such as pot holes--so the researchers can apply them to future robot design.
The goal is to eventually design the real thing, a robot that can cover rough terrain in dangerous circumstances--such as in the military, law enforcement or in space exploration. For humans, the knowledge might help improve prosthetic devices. "Hopefully, we could produce better prosthetic devices than the ones we now have," Schmitt says.
At this stage of the project, Schmitt, 36, doesn't actually work hands-on with the insects. Rather, his role is in developing computer locomotion models that use the animals as a foundation. For example, he began with the idea that guinea hens change their leg angle and leg length at touch-down to recover from drops in the terrain.
"Since the basic, vertical-plane locomotion model I am using [is] valid for a wide range of animals ranging from cockroaches to humans, I then looked to the cockroach for some ideas as to how the leg length should change during the time it touches the ground, and how the leg angle at touch-down should vary in response to a change in ground height," he explains.
His research colleague, Robert Full at the University of California, Berkeley, works directly with the cockroaches. "His work has focused on examining the muscle activation that occurs in cockroach legs as they run," Schmitt says. "I haven't yet had the chance to visit [Full's lab]. I do know that as part of the initiation, he often has visitors to his lab hold a cockroach. While I'm a big fan of how they run, I'd probably not be as thrilled to be holding one. Yet, if I get the chance, I'm sure that I will."
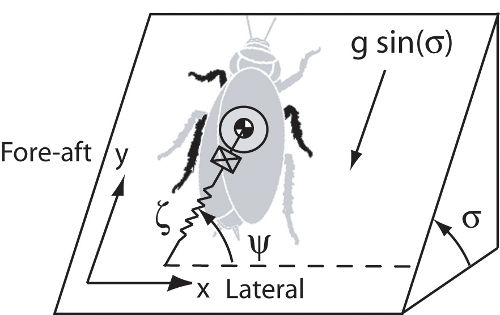 Illustration of the reduced-order, lateral-plane model utilized for investigating locomotion performance on inclines. The cockroach is modeled by a point mass and the forces produced by the tripod of legs of the cockroach are modeled with a single, actuated linear spring. Credit: John Schmitt / Oregon State University Illustration of the reduced-order, lateral-plane model utilized for investigating locomotion performance on inclines. The cockroach is modeled by a point mass and the forces produced by the tripod of legs of the cockroach are modeled with a single, actuated linear spring. Credit: John Schmitt / Oregon State University |
"Having a father who was a mechanical engineer, and who got to work on cool projects such as fighter jets was certainly an inspiration for becoming a mechanical engineer," he says.
His interest in science grew out of an aptitude for math and a fondness for solving logic puzzles. It's not difficult to see how these childhood interests evolved into an engineering career, with an emphasis on research.
"As a kid, trying to figure out how things work is primarily a difficult logic puzzle," he says. It's quite interesting taking items apart and seeing how the individual components fit together to produce the finished product. Becoming an engineer, however, requires the math to figure out why components work as they do--and how you can utilize that knowledge to design them better."
He found his earliest locomotion "models" in the creek that ran near his childhood home. "I was always fascinated by the water striders and their ability to stay afloat and skim across the surface of the water," he says. "I had no idea how they were able to stay on top of the water, and be able to move so fast with just a simple motion. It's only in the past few years that we've learned how water striders utilize water surface tension to effectively row across the water surface.
"In terms of my interest in locomotion, that was certainly my first inspiration for wanting to figure out how incredibly simple biological organisms were able to perform remarkable feats, feats that, in most cases, have yet to be replicated or fully understood by the scientific community," he adds. "Nature is full of these types of puzzles, and as scientists, we are only beginning to scratch the surface of our understanding of how animals and insects achieve their level of performance."
No entries found