Communications of the ACM
Pioneering Seac Computer Remembered on 60th Anniversary

Edith Marden, a computer programmer at the U.S. National Bureau of Standards, operates the Standards Electronic Automatic Computer (SEAC) during the 1950s.
Credit: NIST
Sixty years ago this week, the National Bureau of Standards (now known as the National Institute of Standards and Technology, or NIST) informed the nation about the dedication of the first programmable computer in U.S. history, the Standards Electronic Automatic Computer (SEAC). The revolutionary device moved information as sound wave pulses traveling through 64 mercury-filled glass tubes—in an early data-storage system known as acoustic delay. Each tube had a quartz crystal at both ends, one serving as a transmitter and the other as a receiver. Sound pulses were sent and received repeatedly in a closed loop, recirculating the data patterns they carried and essentially, storing them. It was the electronic equivalent of repeating a telephone number to oneself from the time it is found in the directory until it is dialed.
SEAC had the equivalent of 6,000 bytes of storage (by comparison, today's home computer hard drive has approximately 11 billion bytes). According to "Measures for Progress: A History of the National Bureau of Standards" by R.C. Cochrane (Arno Press, 1976), SEAC "could add or subtract pairs of 11-digit numbers 1,000 times a second, or multiply and divide them 330 times a second." The book also states that "failure of one of its [SEAC's] more than 100,000 connections and components, even for a millionth of a second, would result in a computer malfunction. Yet, often operating nonstop, 7 days a week, SEAC performed for 4,000 hours in its first 9 months without a malfunction." Among the computer's many tasks: computations for the U.S. military and the Atomic Energy Commission; calculations on electronic circuit design and for optical lenses; statistical sorting and tabulating for Social Security and the Census Bureau; and processing of data from studies of crystal structure.
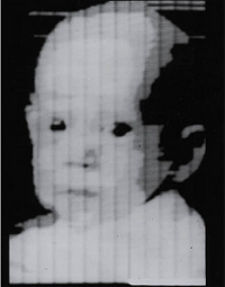 The first digital photo, taken by Russell Kirsch of NBS in 1957, shows Kirsch's three-month-old son, Walden. e Credit: Listverse The first digital photo, taken by Russell Kirsch of NBS in 1957, shows Kirsch's three-month-old son, Walden. e Credit: Listverse |
SEAC served its customers faithfully until 1964 when it was replaced by more advanced computers. In 14 years of active duty, it handled problems and computations in areas such as meteorology, linear programming, optics, navigation, statistics, physics, accounting and manufacturing.
No entries found